Step 1: Pull a Docker Image from docker registry
To illustrate how to commit changes, you first need to have an image to work with. In this article, we work with the latest Ubuntu image for Docker. Download the image from Docker’s library with:
sudo docker pull centosCopy IMAGE ID for later use.
Step 2: Deploy the Container
Add the IMAGE ID to the command that will create a container based on the image:
docker run -it 0d120b6ccaa8 bin/bash
The
–itoptions instruct the container to launch in interactive mode and enable a terminal typing interface. Upon executing the command, a new container launches and moves you to a new shell prompt for working inside of it.Step 3: Modify the Container
Now that you are in the container, you can modify the image. In the following example, we add the git software for network discovery and security auditing:
yum install nmap
or
you can install git as well with below command
yum install git
The command will download the Nmap package and install it inside the running container.
You can verify the installation by running:
nmap --versionThe output shows you that Nmap version 7.70 is installed and ready to use.
Once you finish modifying the new container, exit out of it:
exitPrompt the system to display a list of launched containers:
sudo docker ps -aYou will need the CONTAINER ID to save the changes you made to the existing image. Copy the ID value from the output.
Step 4: Commit Changes to Image
Finally, create a new image by committing the changes using the following syntax:
sudo docker commit [CONTAINER_ID] [new_image_name]Therefore, in our example it will be:
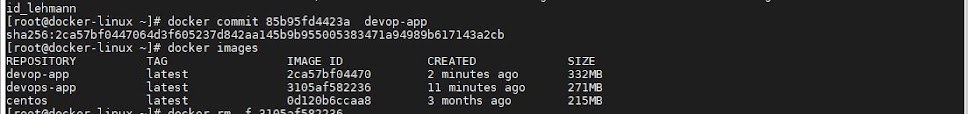
docker commit 85b95fd4423a devop-appWhere 85b95fd4423a is the CONTAINER ID and devop
-appis the name of the new image.Your newly created image should now be available on the list of local images. You can verify by checking the image list again:
sudo docker images
Conclusion
Now that you have learned how to commit changes to a Docker image and create a new one for future uses, take a look at our tutorial on how to set up and use Private/public Docker Registry




No comments:
Post a Comment